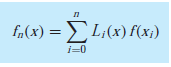A recent addition to R is the pipe-forwarding mechanism (%>%) within the magrittr package. This is extremely useful when using the dplyr, ggvis, and tidyr packages, among others. Pipe forwarding is an alternative to nesting that yields code that can be read from top to bottom. Here we demonstrate an example that compares traditional (nested) dplyr function calls to the new pipe operator.
miércoles, 29 de mayo de 2019
jueves, 23 de mayo de 2019
Parallel with R. Example with snow
Snow provides support for easily executing R functions in parallel. Most of the parallel execution functions in snow are variations of the standard lapply() function, making snow fairly easy to learn. To implement these parallel operations, snow uses a master/ worker architecture, where the master sends tasks to the workers, and the workers execute the tasks and return the results to the master.
The basic cluster creation function is makeCluster() which can create any type of cluster. snow includes a number of functions that we could use, including clusterApply(), clusterApplyLB(), and parLapply(). For this example, we’ll use clusterApply(). You call it exactly the same as lapply(), except that it takes a snow cluster object as the first argument. We also need to load MASS on the workers, rather than on the master, since it’s the workers that use the “Boston” dataset.
We’ll use snow.time() to gather timing information about the overall execution. We will also use snow.time()’s plotting capability to visualize the task execution on the workers.
martes, 19 de marzo de 2019
ARS (Cartesian)
ARS is a basic reservoir simulation spreadsheet. With ARS you can do examples
considering the follow features:
-One dimension
-One phase (oil)
-Incompressible or Slightly compressible fluid
-Rock porosity constant or depending of pressure
-5 different types of boundary conditions
-One well (specified production rate or specified flowing pressure)
miércoles, 25 de octubre de 2017
Reservoir Engineering Tools Android App Tutorial
Reservoir Engineering tools
Android App with Equation of state, Fluid flow in porous media, Reservoir Simulation (One phase-1D) and Waterflooding
Download it in Playstore
jueves, 27 de abril de 2017
Bisection method, Java code
The bisection method, which is alternatively called binary chopping, interval halving, or Bolzano’s method, is one type of incremental search method in which the interval is always divided in half. If a function changes sign over an interval, the function value at the midpoint is evaluated. The location of the root is then determined as lying at the midpoint of the subinterval within which the sign change occurs. The process is repeated to obtain refined estimates. A simple algorithm for the bisection calculation is listed in the following figure.
Reference; Numerical Methods for Engineers. Steven C. Chapra and Raymond P. Canale
martes, 25 de abril de 2017
Lagrange Polynomial Java code
The Lagrange interpolating polynomial is simply a reformulation of the Newton polynomial
that avoids the computation of divided differences. It can be represented concisely as
where
Suscribirse a:
Entradas (Atom)